Free Fall Equation Calculus. Gravity will accelerate a falling object, increasing its velocity by 9.81 m/s 2 (or or 32 ft/s 2) for every second it experiences free fall. Differential equations → polynomial function:
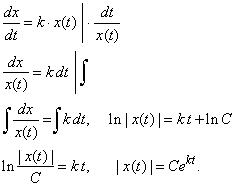
H= \( \frac{1}{2}gt^2 \) v²= 2gh; Using calculus to derive the freefall formula. Applications of differential equations →
An interesting application of equation 3.3.2 through equation 3.5.22 is called free fall, which describes the motion of an object falling in a gravitational field, such as near the surface of earth or other celestial objects of planetary size.
The equation \displaystyle{t}=\frac{\sqrt{{h}}}{{4}} is the time it takes for the elevator. Distance (height) of free fall; Substituting the known values in along with the value for g, reduces the equation to: If = 0 at t=0, calculus can be used to solve eq.